In the dynamic realm of construction, one thing remains constant: the relentless pursuit of accuracy and efficiency. Traditionally, construction managers and overseers have relied on land surveying techniques that, while effective, often demanded significant time, labor, and resources. However, the winds of change have ushered in an innovative technique that is redefining the boundaries of surveying and mapping — the deployment of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, or UAVs.
As the demand for faster data acquisition and highly accurate measurements escalates, the world of UAV surveying and mapping is expanding at an unprecedented rate. This flying marvels not only streamline the intricate process of gathering topographic surveys but also offer a fresh perspective, literally, from a bird’s eye view. So, how exactly does drone mapping fit into the larger jigsaw of construction management, and why is it quickly becoming an indispensable tool for industry professionals?
Journey with us as we delve into the mechanics, benefits, and applications of drone mapping in the world of construction. Whether you’re a seasoned construction manager, an overseer looking to enhance your site assessment techniques, or merely curious about the integration of technology in construction, this guide will provide valuable insights into the transformative power of drones for mapping and surveying.
The Basics of Drone Mapping
Drones, once primarily a mainstay of military operations and hobbyist enthusiasts, have now taken center stage in a myriad of professional applications. When we speak of drone mapping in the context of construction, we are referring to the systematic acquisition of high-resolution aerial images, which are then processed and converted into detailed maps and models of a particular terrain or area. But what sets drone mapping apart from traditional survey methods? Let’s break it down.
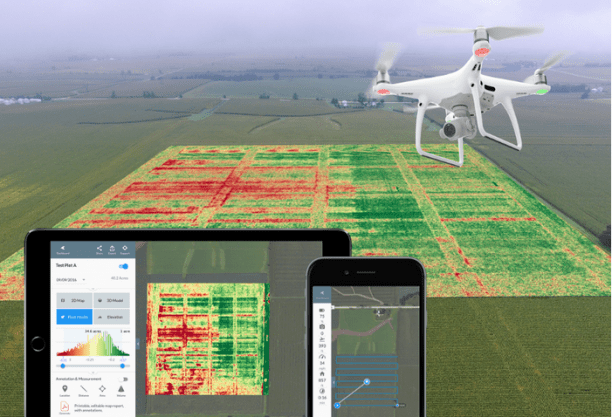
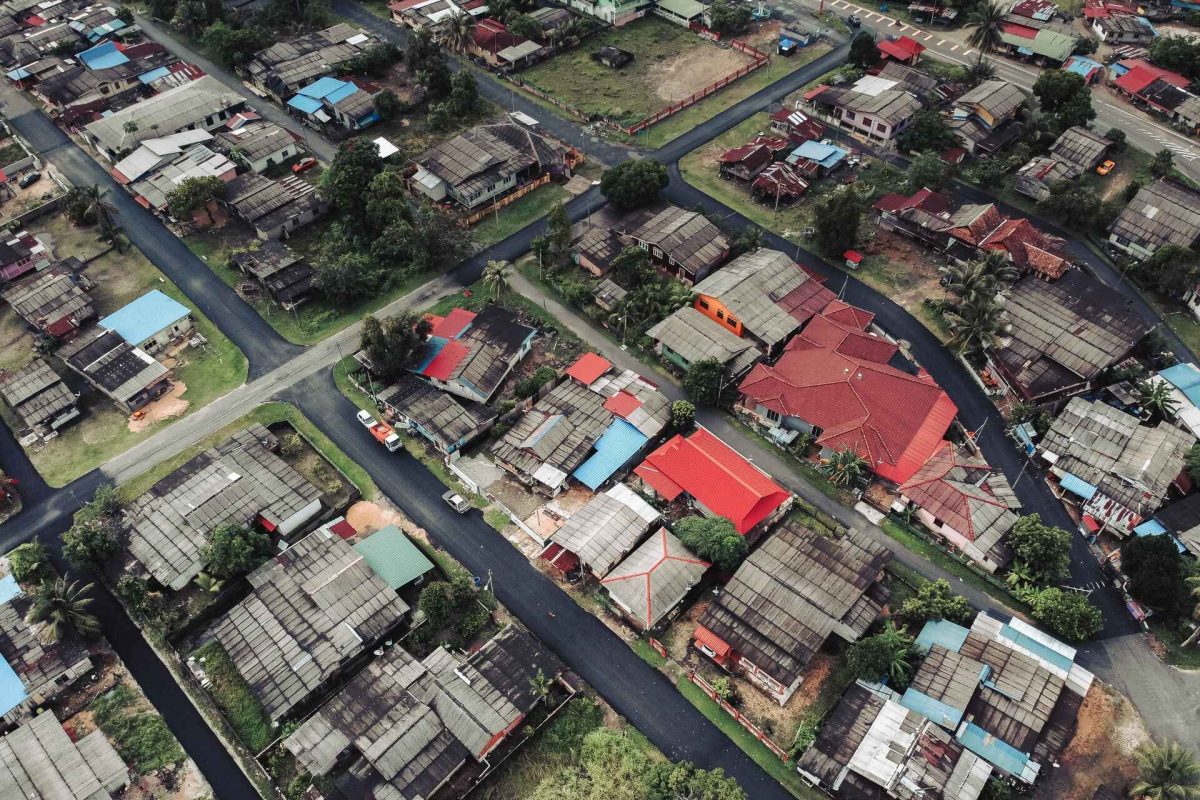
What is Drone Mapping? At its core, drone mapping is the practice of using drones, equipped with high-resolution cameras, to capture aerial imagery. As the drone flies over a specific area, it takes multiple overlapping photos of the ground below. Through sophisticated software, these images are then stitched together to create comprehensive, highly accurate aerial maps and 3D models.
Revolutionizing Traditional Topographic Surveys: Traditional topographic surveys, while reliable, often involve tedious manual measurements and can be resource-intensive. Drones for mapping and surveying, on the other hand, provide an aerial perspective, allowing for the capture of vast areas in significantly less time. This not only expedites the surveying process but also reduces potential human errors.
Benefits of Using Drones for Mapping and Surveying:
- Speed & Efficiency: Covering large areas becomes more feasible with drones. What might take days or even weeks manually can be accomplished in a few hours with a drone.
- Highly Accurate Data: With the integration of advanced technologies like RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) and GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System), drones can produce highly accurate topographic data, rivaling, and often surpassing, traditional methods.
- Flexibility: Drones can be deployed in diverse terrains and conditions where manual surveys might be challenging or unsafe.
- Cost-Effective: Given the rapid data acquisition and reduced manpower needs, drones often present a more cost-efficient approach to mapping and surveying.
As we delve deeper into the nuances of drone mapping, it becomes evident that the synergy between cutting-edge technology and construction management offers unprecedented advantages. The aerial surveying capabilities of drones, coupled with their efficiency, make them a compelling choice for modern construction projects.
Types of Drones Used for Mapping
The world of drones is diverse, with each type uniquely engineered for specific functions. When it comes to surveying and mapping, especially within the construction domain, certain drones are more favored due to their specific features and capabilities. Here, we’ll focus on the primary types of drones utilized for mapping purposes and shed light on why certain models are preferred over others.
Fixed-Wing Drones: A Closer Look
- Overview: Unlike their multi-rotor counterparts, fixed-wing drones are designed with rigid wings that provide lift. Resembling a traditional airplane in design, these drones can cover vast distances and remain airborne for extended periods.
- Advantages in Mapping:
- Endurance and Range: Due to their aerodynamic design, fixed-wing drones can survey large areas without needing frequent battery changes.
- Efficiency: These drones can cover vast areas quickly, making them ideal for mapping expansive construction sites or projects.
- Stability: Their design ensures stable flight, ensuring consistent and high-quality aerial map data collection.
Multi-Rotor Drones:
- Overview: These are the drones most people are familiar with, having multiple rotors (usually four) that allow them to hover and maneuver with precision.
- Mapping Applications: While they may not have the same range as fixed-wing drones, multi-rotor drones excel in areas that require detailed imaging or when operating in confined spaces. Their ability to hover provides the opportunity for in-depth site assessments.

Hybrid Drones:
- Overview: As the name suggests, hybrid drones combine elements from both fixed-wing and multi-rotor designs. They can take off and land vertically (like multi-rotor drones) and transition to horizontal flight (like fixed-wing drones).
- Mapping Applications: Ideal for projects that require the versatility of both drone types, offering endurance and detailed data acquisition.
Selecting the Right Drone for Your Mapping Needs:
- Terrain & Size of the Project: Larger, open terrains are best suited for fixed-wing drones, while smaller sites or those with obstacles may benefit from the precision of multi-rotor drones.
- Resolution Requirements: For projects that demand high-resolution imagery, the stability and hover capability of multi-rotor drones can be invaluable.
- Budget & Training: While fixed-wing drones might offer efficiency for large projects, they can be pricier and require more specialized training.
In conclusion, the drone you choose for mapping in construction projects largely depends on the specific requirements and challenges of the site. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of each type is essential for optimal data collection and, ultimately, the success of the surveying and mapping endeavor.
The Process of Drone Mapping
Understanding the drone’s capabilities is just one piece of the puzzle; the real magic unfolds when we dive into the intricate process of drone mapping itself. While the technology might seem overwhelmingly advanced, the process, when broken down, follows a systematic and logical progression. Let’s journey through the steps involved in drone mapping from takeoff to the final map creation.
1. Pre-flight Planning:
- Site Assessment: Before a drone takes to the skies, it’s crucial to evaluate the area for obstacles, safety concerns, and specific areas of interest.
- Flight Path Design: Utilizing specialized software, operators chart out a flight path that the drone will follow. This ensures comprehensive coverage and high-quality data capture.
2. Taking Off and Flight Execution:
- Automated Flight: Once launched, most drones for surveying operate on an autonomous mode, strictly following the pre-defined path to capture aerial images.
- Real-time Monitoring: Even in automated flight, operators monitor the drone’s progression, ensuring it’s on course and adjusting the path if unexpected obstacles arise.
3. Capturing Aerial Imagery:
- Overlapping Photos: As the drone flies overhead, it doesn’t just take random pictures. It captures a series of overlapping images, which are vital for creating a cohesive and detailed aerial map.
- High-resolution Capture: Drones equipped with advanced cameras ensure high-resolution image capture, a pivotal factor in the accuracy of the resultant maps.
4. Data Processing:
- Image Stitching: Once the flight is complete, the multiple captured images are imported into mapping software. These photos are then ‘stitched’ together, using common points in each image, to form a singular, large-scale image of the surveyed area.
- Topographic Data Extraction: Sophisticated algorithms analyze the stitched image to extract topographic data, identifying variations in terrain, structures, and other significant features.
5. Map and Model Creation:
- 2D Aerial Maps: For many construction applications, a 2D aerial map suffices, providing a detailed bird’s eye view of the project site.
- 3D Models: For more intricate projects, the captured data can be used to create 3D models, offering a detailed and interactive representation of the terrain and its features. This is especially useful for understanding elevation changes, volume measurements, and spatial relationships between various elements.
6. Analysis and Application:
- Site Assessment: With the aerial maps and models in hand, construction managers can undertake comprehensive site assessments, plan logistics, and identify potential challenges.
- Integration with Other Data: Often, the drone’s survey data is integrated with other information sources, such as GIS (Geographic Information Systems), to provide a holistic understanding of the project terrain.
In Closing…
The process of drone mapping, while systematic, harnesses the prowess of advanced technology at every step. From the moment a drone takes flight to the time a detailed map is generated, there’s a seamless blend of automation, precision, and technology, ensuring construction managers receive highly accurate, real-time data that can significantly enhance project outcomes.
Volume Measurement and 3D Maps
Within the vast spectrum of applications for drone mapping in construction, two areas stand out for their profound impact on project planning and management: volume measurement and the creation of 3D maps. These functionalities not only streamline operations but also introduce unprecedented accuracy, which can be pivotal in resource allocation, cost estimation, and risk management.
Understanding Volume Measurement with Drones:
- What it Entails: Volume measurement in construction refers to the quantification of materials on site, such as stockpiles of gravel, sand, or other resources. Accurate volume measurements can dictate resource allocation, cost forecasting, and logistical planning.
- The Drone Advantage: Unlike traditional methods, which often required manual measurements and were susceptible to errors, drones offer an aerial perspective, capturing the entire stockpile and its nuances.
- High Accuracy: By capturing multiple vantage points, drones ensure that no part of the stockpile remains obscured, leading to more accurate measurements.
- Time-Efficiency: What might have taken hours or days can now be achieved within a fraction of the time, without compromising on precision.
Creating 3D Maps: A New Dimension in Surveying:
- Beyond the 2D Perspective: While 2D maps provide an expansive bird’s eye view, 3D models offer depth, elevation, and a more immersive understanding of terrains.
- How it Works: Using the overlapping photos captured by drones, specialized software constructs 3D models by identifying common reference points across images, effectively ‘stitching’ them into a three-dimensional representation.
- Topographic Details: These models don’t just offer a visual advantage; they embed crucial topographic data, highlighting elevation changes, slopes, and other pivotal terrain features.
- Interactive Engagement: Many 3D mapping solutions allow users to interact with the model, rotating, zooming, and even simulating potential construction modifications.
Applications in Construction:
- Site Analysis: With 3D maps, construction managers can undertake a multi-dimensional analysis, understanding how different elements of the site interact and identifying potential challenges.
- Logistical Planning: From determining the best routes for machinery to gauging the spatial relationships between various construction elements, 3D models inform logistics.
- Resource Management: Volume measurements derived from drone surveys inform managers about the materials on site, helping in efficient allocation and reducing wastage.
Volume measurement and 3D maps epitomize the transformative power of drone mapping in construction. They embody the shift from labor-intensive, time-consuming manual processes to rapid, highly accurate automated solutions. For construction managers and overseers, this means better decision-making, cost-efficiency, and proactive problem-solving, all driven by the detailed insights offered by drone-generated data.
Advantages of Drone Mapping in Construction
The advent of drones in the construction arena is more than just the integration of cutting-edge technology; it represents a paradigm shift in how construction sites are viewed, assessed, and managed. While we’ve touched upon some of these advantages in our previous sections, it’s essential to consolidate and understand the comprehensive benefits of drone mapping in construction.
1. Time Efficiency:
- Rapid Data Acquisition: Drones can cover vast areas in a short span, significantly reducing the time required for site surveys.
- Instant Insights: With real-time data capture, construction managers can access and analyze aerial surveying data almost immediately after the drone completes its flight.
2. Enhanced Accuracy:
- Precision Imaging: Advanced cameras and sensors ensure that drones capture high-resolution images, which translate into highly accurate maps and models.
- Consistent Results: Automated flight paths and image capturing processes ensure consistency across different survey sessions.
3. Cost Savings:
- Reduced Manpower Needs: Drones can cover areas that might have required multiple surveyors if done manually.
- Fewer Errors: The high accuracy of drone mapping translates to fewer mistakes, which can be expensive in the construction world.
4. Safety Improvements:
- Remote Surveys: Drones can safely survey hazardous or inaccessible areas, reducing the risk of accidents or injuries to surveying personnel.
- Detailed Risk Assessments: With comprehensive aerial maps, potential safety hazards can be identified and addressed proactively.
5. Comprehensive Data Integration:
- Versatile Outputs: From 2D aerial maps to interactive 3D models, drones offer a range of outputs to suit various project requirements.
- GIS Integration: Drone-derived data can seamlessly integrate with Geographic Information Systems, allowing for richer site analysis and insights.
6. Flexible Application:
- Varied Terrains: Whether it’s rugged terrains, wetlands, or densely populated sites, drones can navigate and capture data with ease.
- Multiple Project Phases: Drones are useful not just in the pre-construction phase but also during construction and post-construction for monitoring and documentation purposes.
7. Eco-friendly:
- Minimal Disturbance: Drone flights are non-intrusive, ensuring minimal disturbance to the environment and local ecosystems.
- Resource Optimization: Accurate measurements mean fewer resources go to waste, promoting sustainable construction practices.
Drone mapping in construction is not just a trend but a testament to the industry’s evolution. Embracing drones means embracing efficiency, accuracy, safety, and innovation. For construction managers and overseers, this integration not only simplifies tasks but elevates the quality and precision of their projects, ensuring they stay at the forefront of modern construction practices.
Things to Consider When Adopting Drone Surveying
Transitioning to drone-based surveying might be an exciting proposition for many construction managers and overseers, but it’s not a process to be taken lightly. While the advantages are numerous, understanding the considerations and potential challenges is crucial for seamless integration. Here’s a list of vital points to keep in mind when adopting drone surveying for construction projects.
1. Legal and Regulatory Concerns:
- Flight Permissions: Different countries and regions have varying regulations regarding drone flights, especially in commercial contexts. It’s crucial to understand and acquire the necessary permits.
- No-fly Zones: Some areas, especially near airports, military bases, or other critical infrastructure, may be off-limits for drones.
2. Training and Expertise:
- Pilot Training: Flying a drone, especially in a commercial setting, requires skill. Investing in proper training for operators is essential.
- Data Interpretation: Understanding the data captured by drones, from aerial images to 3D maps, might require training or hiring experts who can interpret and integrate this data effectively.
3. Hardware and Software Choices:
- Selecting the Right Drone: As discussed earlier, the choice of drone—fixed-wing, multi-rotor, or hybrid—will depend on the specific needs of the project.
- Mapping Software: The software used to process and analyze drone images plays a crucial role in the quality of the output. It’s vital to choose software that aligns with the project’s requirements.
4. Data Privacy and Security:
- Data Handling: Drones capture a vast amount of data. Proper storage, handling, and protection of this data are essential to prevent breaches or misuse.
- Neighboring Properties: While surveying a construction site, drones might inadvertently capture images of neighboring properties. Being mindful of privacy concerns and addressing any issues proactively is vital.
5. Environmental Factors:
- Weather Conditions: Drones, especially lightweight ones, can be affected by weather conditions like strong winds, rain, or snow. Planning flights while keeping the weather in mind is essential.
- Flight Time and Battery Life: Depending on the drone model, battery life can vary. Managers need to plan flights accordingly, ensuring that the drone can cover the desired area within its operational time.
6. Integration with Existing Processes:
- Workflow Adaptation: Adopting drone surveying might require some changes in existing workflows, especially in how data is collected, processed, and used.
- Stakeholder Communication: Keeping all project stakeholders, from team members to clients, informed about the shift to drone-based surveying and its implications is vital.
7. Return on Investment (ROI):
- Upfront Costs: While drone surveying can lead to significant savings in the long run, the initial investment in equipment, software, and training can be substantial.
- Long-term Benefits: It’s essential to weigh the upfront costs against the long-term benefits in terms of time saved, increased accuracy, and other advantages.
Adopting drone surveying is a strategic decision that comes with its set of challenges and considerations. However, with the right planning, understanding, and investment, the rewards can be substantial. Being well-informed and proactive can ensure a smooth transition to this modern, efficient, and highly beneficial surveying methodology.
Conclusion
In the rapidly evolving world of construction, staying ahead of the curve is not just about adopting the latest technologies, but understanding their profound impact and harnessing them effectively. Drones, or UAVs, have shifted from being mere gadgets to essential tools, transforming how we perceive, plan, and execute construction projects.
Through drone mapping and surveying, construction overseers and managers are now empowered with a bird’s eye view, offering real-time, highly accurate insights into their sites. Whether it’s the precision of volume measurements, the depth of 3D maps, or the efficiency of rapid aerial surveys, the advantages are undeniable. But, as with any technology, its true power lies in its responsible and informed application.
In embracing UAV surveying and mapping, the construction industry takes a significant leap forward. It’s a journey from traditional, time-intensive methods to a future where accuracy, efficiency, and safety are paramount. And while the path might be dotted with considerations, from regulatory concerns to training needs, the destination promises unparalleled advancements for the world of construction.
As we conclude this exploration into the realm of drone mapping, the message is clear: the future of construction surveying is not just up in the air—it’s soaring with drones, mapping out a clearer, more efficient, and detailed path forward.




